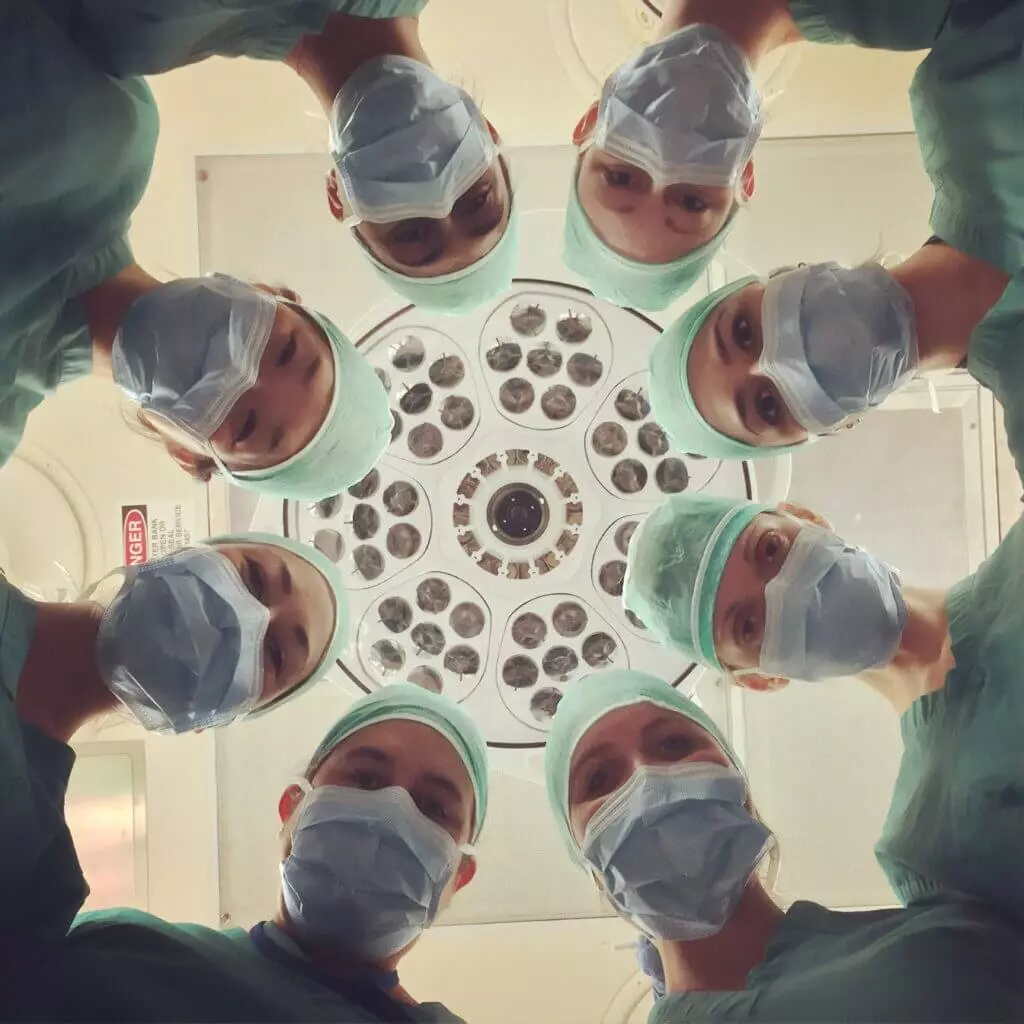
Researchers from the Harvard Medical School have developed an artificial intelligence (AI) based tool that can rapidly decode the DNA of a brain tumor, providing crucial information about its molecular identity during surgery. This information, which previously could take days or weeks to obtain through traditional methods, can now be accessed instantly.
By knowing the molecular type of a tumor, neurosurgeons can make critical decisions during the surgery, such as the amount of brain tissue to be removed or the placement of medications directly into the brain to destroy the tumors, all in real-time while the patient is still on the operating table. This discovery could bring significant advances in research for personalized treatments for one of the most deadly forms of cancer.
According to statements from the study’s lead author, Assistant Professor of Biomedical Informatics Kun-Hsing Yu from the Blavatnik Institute at Harvard, even in state-of-the-art clinical practice, it is not possible to perform the molecular profiling of tumors during surgery. However, their team has developed an AI-based tool that overcomes this challenge by extracting previously untapped biomedical signals from frozen pathological samples.
The research team stated that the tool, called CHARM (Cryosection Histopathology Assessment and Review Machine), is freely available to other researchers. However, it still needs to be clinically validated through tests in real-world settings and must receive authorization from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) before being implemented in hospitals.
Echipa de cercetare a menționat că instrumentul, numit CHARM (Cryosection Histopathology Assessment and Review Machine), este disponibil gratuit pentru alți cercetători. Cu toate acestea, acesta trebuie încă validat clinic prin teste în medii reale și trebuie să primească autorizația de la Autoritatea Americană de Reglementare a Medicamentelor și Alimentelor (FDA) înainte de a fi implementat în spitale.
Follow us on social media:
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/securemenow/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/securmenow
We offer Web Design services. Contact us